Difference between revisions of "MQP:Security Analysis Data Model"
From JimboWiki
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Requirements== | ==Requirements== | ||
| − | *The structure should be easy to traverse | + | *The structure should be easy to search and traverse |
| − | + | *The structure must contain a representation of each code element analyzed along with the permissions required by each code element | |
| − | + | *Each permission requirement must provide a complete path to where the requirement originated | |
| − | + | *Each permission requirement must provide the names of the methods that determined it | |
| − | + | *The structure must hold ''"Management Data"'' - policy information that comes from absolute sources (for example, the security policy of a given server or user input at runtime) | |
| − | + | *There must be a way to calculate the resultant set of policy | |
| − | *The structure | + | *There should be a way to optimize the resultant set of policy by analyzing overlapping permission requirements |
| − | ** | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
==Design== | ==Design== | ||
*Data storage | *Data storage | ||
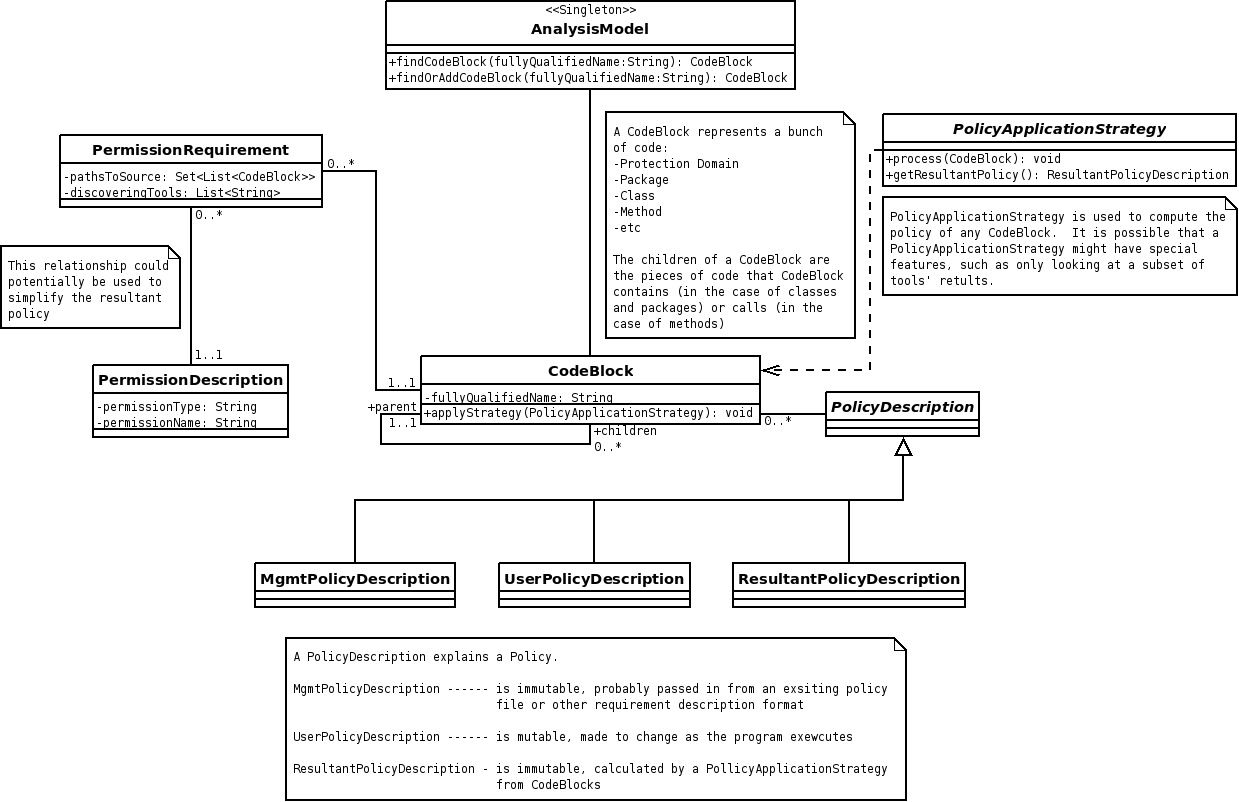
| − | **A top level singleton class, ''AnalysisModel'', contains each | + | **A top level singleton class, ''AnalysisModel'', contains each CodeBlock |
| − | ** | + | ***'''CodeBlock''' - Any grouping of code: package, protection domain, class, method, etc. |
| − | ** | + | ***The CodeBlock contains any number of PermissionRequirements and any number of PolicyDescriptions |
| − | ** | + | ****'''PermissionRequirement''' - Tells what permission is required (using a ''PermissionDescription''), the path to get to the permission checking call, and a list of tools that agree on this requirement |
| − | + | ****'''PolicyDescription''' - Describes a set of policy | |
| − | * | + | *Data Retrieval |
| − | ** | + | **Search is performed from the AnalysisModel - any CodeBlock can be found this way, as the AnaysisModel contains each CodeBlock |
| − | *** | + | **Traversal of the call structure is performed from any CodeBlock - each has a list of children and a reference back to its parent (if any) |
| − | ** | + | **Traversal of the permission structure is performed from any PermissionRequirement (via a CodeBlock) - each PermissionRequirement has a full trace to the origin of the permission it describes |
| − | ** | + | **Resultant policy calculation uses a PolicyApplicationStrategy, which starts at any CodeBlock, and is passed through all its children, processing permissions as it goes |
| − | + | **Policy optimization can occur if more than one PermissionRequirement exists for a given PermissionDescription | |
| − | ** | + | |
[[Image:AnalysisModel.png|frame|left|Security Analysis Model]] | [[Image:AnalysisModel.png|frame|left|Security Analysis Model]] | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 3 September 2008
Contents |
|
Overview
In order to provide the results of analysis, a data structure was devised to store the results.
Requirements
- The structure should be easy to search and traverse
- The structure must contain a representation of each code element analyzed along with the permissions required by each code element
- Each permission requirement must provide a complete path to where the requirement originated
- Each permission requirement must provide the names of the methods that determined it
- The structure must hold "Management Data" - policy information that comes from absolute sources (for example, the security policy of a given server or user input at runtime)
- There must be a way to calculate the resultant set of policy
- There should be a way to optimize the resultant set of policy by analyzing overlapping permission requirements
Design
- Data storage
- A top level singleton class, AnalysisModel, contains each CodeBlock
- CodeBlock - Any grouping of code: package, protection domain, class, method, etc.
- The CodeBlock contains any number of PermissionRequirements and any number of PolicyDescriptions
- PermissionRequirement - Tells what permission is required (using a PermissionDescription), the path to get to the permission checking call, and a list of tools that agree on this requirement
- PolicyDescription - Describes a set of policy
- A top level singleton class, AnalysisModel, contains each CodeBlock
- Data Retrieval
- Search is performed from the AnalysisModel - any CodeBlock can be found this way, as the AnaysisModel contains each CodeBlock
- Traversal of the call structure is performed from any CodeBlock - each has a list of children and a reference back to its parent (if any)
- Traversal of the permission structure is performed from any PermissionRequirement (via a CodeBlock) - each PermissionRequirement has a full trace to the origin of the permission it describes
- Resultant policy calculation uses a PolicyApplicationStrategy, which starts at any CodeBlock, and is passed through all its children, processing permissions as it goes
- Policy optimization can occur if more than one PermissionRequirement exists for a given PermissionDescription